key differences between medical billing and medical coding
key differences between medical billing and medical coding
Definition
Medical Billing: The process of submitting and following up on claims with health insurance companies to receive payment for healthcare services.
Medical Coding: The process of translating healthcare diagnoses, procedures, medical services, and equipment into standardized alphanumeric codes (e.g., ICD, CPT, HCPCS).
Role in Healthcare
Billing: Focuses on financial transactions, insurance claims, and patient billing.
Coding: Focuses on transforming medical records into universal codes for insurance and data purposes.
Primary Tasks
Billing:
Creating and submitting claims to insurance providers
Managing claim rejections or denials
Sending patient invoices and collecting payments
- Coding:
Reviewing patient records and doctor’s notes
Assigning proper codes for diagnoses and procedures
Ensuring compliance with coding standards
Skills Required
Billing: Knowledge of insurance policies, billing software, claim submission processes, and patient communication.
Coding: Strong understanding of medical terminology, anatomy, disease processes, and coding systems (ICD-10, CPT, HCPCS).
End Goal
Billing: To secure correct and timely reimbursement from insurance companies and patients.
Coding: To ensure accurate representation of patient care for insurance claims, data analysis, and healthcare statistics.
Work Relationship
Coding comes first → medical coders assign codes.
Billing comes next → billers use those codes to prepare and submit insurance claims.
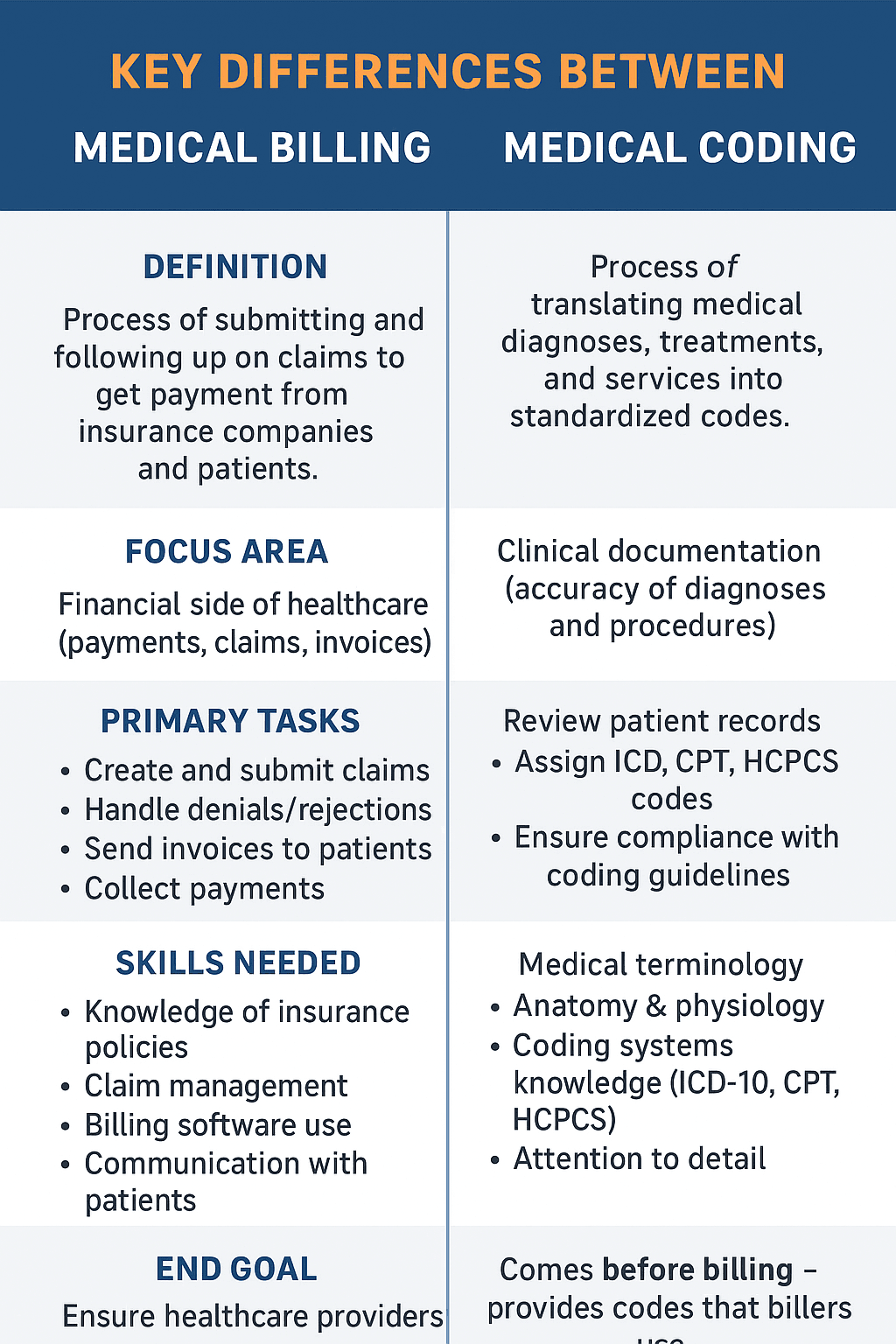
Here’s a clear comparison table for you:
| Aspect | Medical Billing | Medical Coding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of submitting and following up on claims to get payment from insurance companies and patients. | Process of translating medical diagnoses, treatments, and services into standardized codes. |
| Focus Area | Financial side of healthcare (payments, claims, invoices). | Clinical documentation (accuracy of diagnoses and procedures). |
| Primary Tasks | – Create and submit claims – Handle denials/rejections – Send invoices to patients – Collect payments | – Review patient records – Assign ICD, CPT, HCPCS codes – Ensure compliance with coding guidelines |
| Skills Needed | – Knowledge of insurance policies – Claim management – Billing software use – Communication with patients | – Medical terminology – Anatomy & physiology – Coding systems knowledge (ICD-10, CPT, HCPCS) – Attention to detail |
| End Goal | Ensure healthcare providers receive accurate and timely payment. | Ensure accurate documentation of patient care for billing, research, and statistics. |
| Order of Process | Comes after coding – uses codes to prepare claims. | Comes before billing – provides codes that billers use. |